10:44 AM 7/29/2020 - Is this the sign of the "rational" (lab, man-made) rather than the "natural" design of this infection(s) and its pathogen(s)?
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

10:44 AM 7/29/2020
Is this the sign of the "rational" (lab, man-made) rather than the "natural" design of this infection(s) and its pathogen(s)?
"the increased infectivity of the G-form is likely due to a higher rate of profitable binding encounters with the host receptor." - The SARS-CoV-2 Spike Variant D614G Favors an Open Conformational State
| Michael Novakhov - SharedNewsLinks |
|---|
| Emergent SARS-CoV-2 D614G spike mutation more infective due to "open" morphology |
Saved and Shared Stories from Michael_Novakhov | Page
Headlines | Saved and Shared Stories In 250 Brief Posts
___________________________________________________________________
Michael Novakhov - SharedNewsLinks - Latest Post
| Michael Novakhov - SharedNewsLinks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Emergent SARS-CoV-2 D614G spike mutation more infective due to "open" morphology | ||
Researchers from the Los Alamos National Laboratory and Duke Human Vaccine Institute & Department of Surgery demonstrated that globally prevalent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) with the amino acid substitution D614G in the spike protein is much more infective due to profitable binding encounters with the host receptors. Their findings are currently available on the bioRxiv* preprint server.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2 represents a salient global health emergency. This virus infects human cells by utilizing the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the trimeric spike protein to bind to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor found in many cells of the human body. Amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, the emergence of a SARS-CoV-2 variant, which carried the amino acid substitution D614G in the spike protein, has been observed. Very soon, that exact viral strain became globally prevalent. Mechanistically speaking, in the "all-down" spike conformation, all three RBDs of the protomers are in the closed orientation. However, binding of the RBD to ACE2 necessitates the transition of one of the protomers from the closed to an open conformation. Such an infection-capable configuration is referred to as open or "one-up" spike conformation. Consequently, the resulting G-form is considered more infectious in the laboratory conditions and associated with increased viral loads in infected people. To identify the factors that lead to such distinct viral dynamics, a research group from the Los Alamos National Laboratory and Duke Human Vaccine Institute & Department of Surgery in the United States conducted a meticulous mechanistic analysis and obtained some interesting and novel insights. 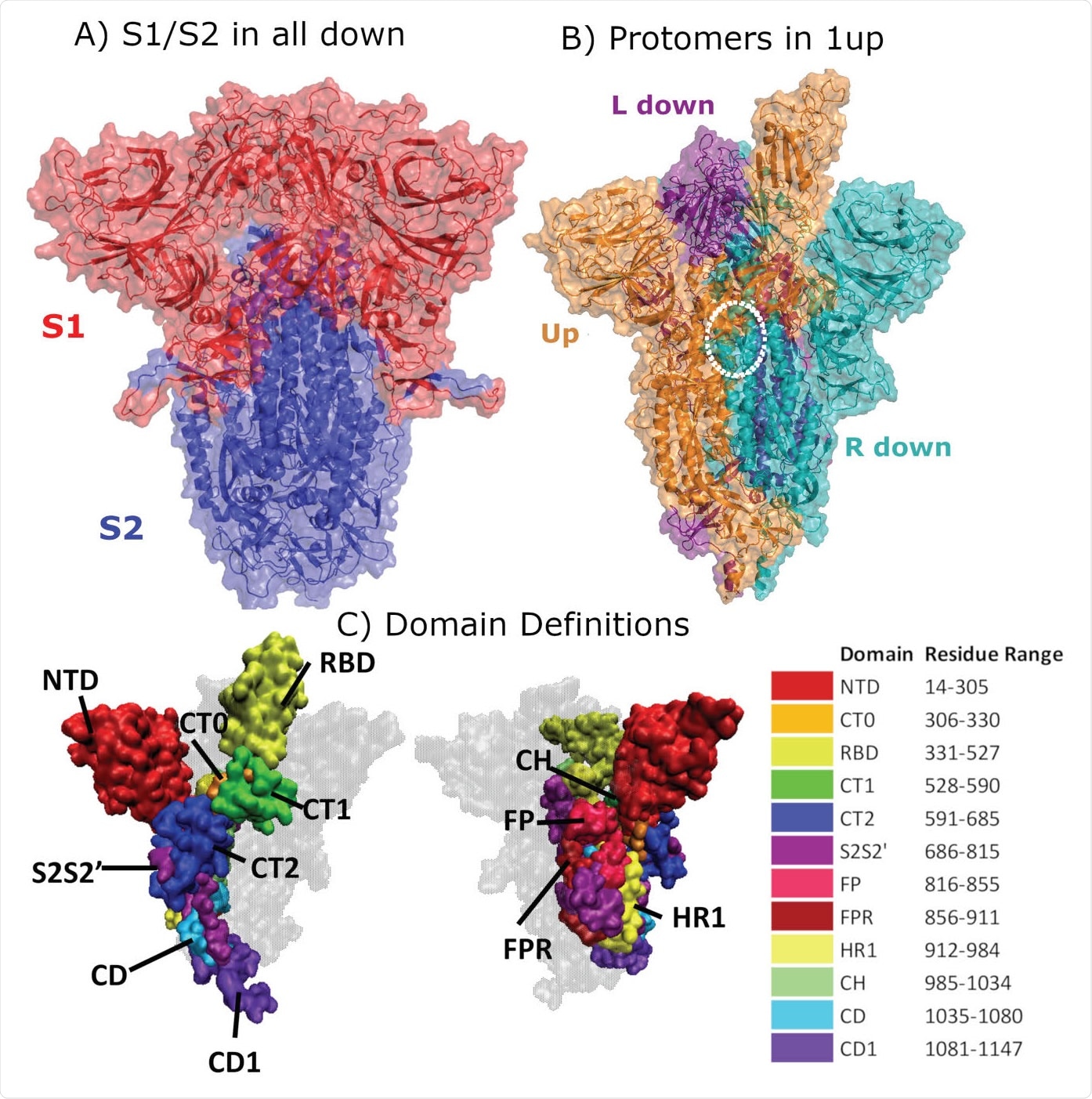 Structural Representation of the Spike protein. (A) The Spike complex is shown in the all-down conformation. Its S1 and S2 subunits are depicted in red and blue. (B) The Spike complex is shown in the one-up conformation. It is composed of three protomers, with the L-down protomer depicted in purple, the Up protomer in orange, and the R-down protomer in cyan. The dashed white circle indicates a D614G site. Here, only one of the three D614G sites are shown. (C) Definition of twelve domains and their residues used for analysis of simulations. It was necessary to define domains for every region for analysis, so some regions may have arbitrarily assigned names or not follow canonical sequence ranges. We display the domains highlighted in the Spike structure, shown from two different perspectives. Definitions of domain abbreviations: NTD, N-Terminal Domain; CT0, C313 Terminal domain 0; RBD, Receptor Binding Domain; CT1, C-Terminal domain 1; CT2, C-Terminal domain 2; S2S2, S1/S2 Cleavage to S2; FP, Fusion Peptide; FPR, Fusion Peptide Region; HR1, Heptad Repeat 1; CH, Center Helix; CD, Connector Domain; and CD1, Connector Domain 1. Images in (A)-(B) were created with PyMol (15); images in (C) were prepared using VMD (16). Structural Representation of the Spike protein. (A) The Spike complex is shown in the all-down conformation. Its S1 and S2 subunits are depicted in red and blue. (B) The Spike complex is shown in the one-up conformation. It is composed of three protomers, with the L-down protomer depicted in purple, the Up protomer in orange, and the R-down protomer in cyan. The dashed white circle indicates a D614G site. Here, only one of the three D614G sites are shown. (C) Definition of twelve domains and their residues used for analysis of simulations. It was necessary to define domains for every region for analysis, so some regions may have arbitrarily assigned names or not follow canonical sequence ranges. We display the domains highlighted in the Spike structure, shown from two different perspectives. Definitions of domain abbreviations: NTD, N-Terminal Domain; CT0, C313 Terminal domain 0; RBD, Receptor Binding Domain; CT1, C-Terminal domain 1; CT2, C-Terminal domain 2; S2S2, S1/S2 Cleavage to S2; FP, Fusion Peptide; FPR, Fusion Peptide Region; HR1, Heptad Repeat 1; CH, Center Helix; CD, Connector Domain; and CD1, Connector Domain 1. Images in (A)-(B) were created with PyMol (15); images in (C) were prepared using VMD (16).Appraising molecular-level impactsIn a nutshell, this study successfully used multifarious replicas of microsecond all-atom simulations in order to probe the molecular-level impact of the amino acid substitution D614G on closed and open states of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein."To elucidate how specific interactions are altered by the D614G substitution, we calculated residue-residue contacts that are formed between subunits of all three protomers", further explain study researchers.Hydrogen bonding interactions of the speculated critical residues were studied in-depth, primarily to observe whether hydrogen bond reduction can lead to a conformational relaxation of the spike protein. Moreover, a global differential contact analysis was also pursued, and the researchers have modeled the impact of highly-flexible glycan ensembles on RBD exposure and epitope shielding with the use of a quantitative measure known as the glycan encounter factor. A higher rate of profitable binding encounters"We found that the D614G substitution was directly associated with far-reaching alterations in inter-protomer interactions and indirectly associated with changes in binding site exposure", study authors state their main finding.More specifically, the G614 form was shown to lead to a rearrangement in residue-residue contacts and hydrogen bonding that would lead to an increased population of the one-up spike ensemble or open conformations. Likewise, a careful analysis of RBD exposure (including the role of highly-flexible glycans) revealed that both the ACE2 binding site and critical neutralizing antibody epitopes in the RBD are definitely more accessible in the one upstate. As a consequence, the increased infectivity of the aforementioned G-form can be observed, likely arising due to a much higher rate of profitable binding encounters with the receptor located at the host cells. 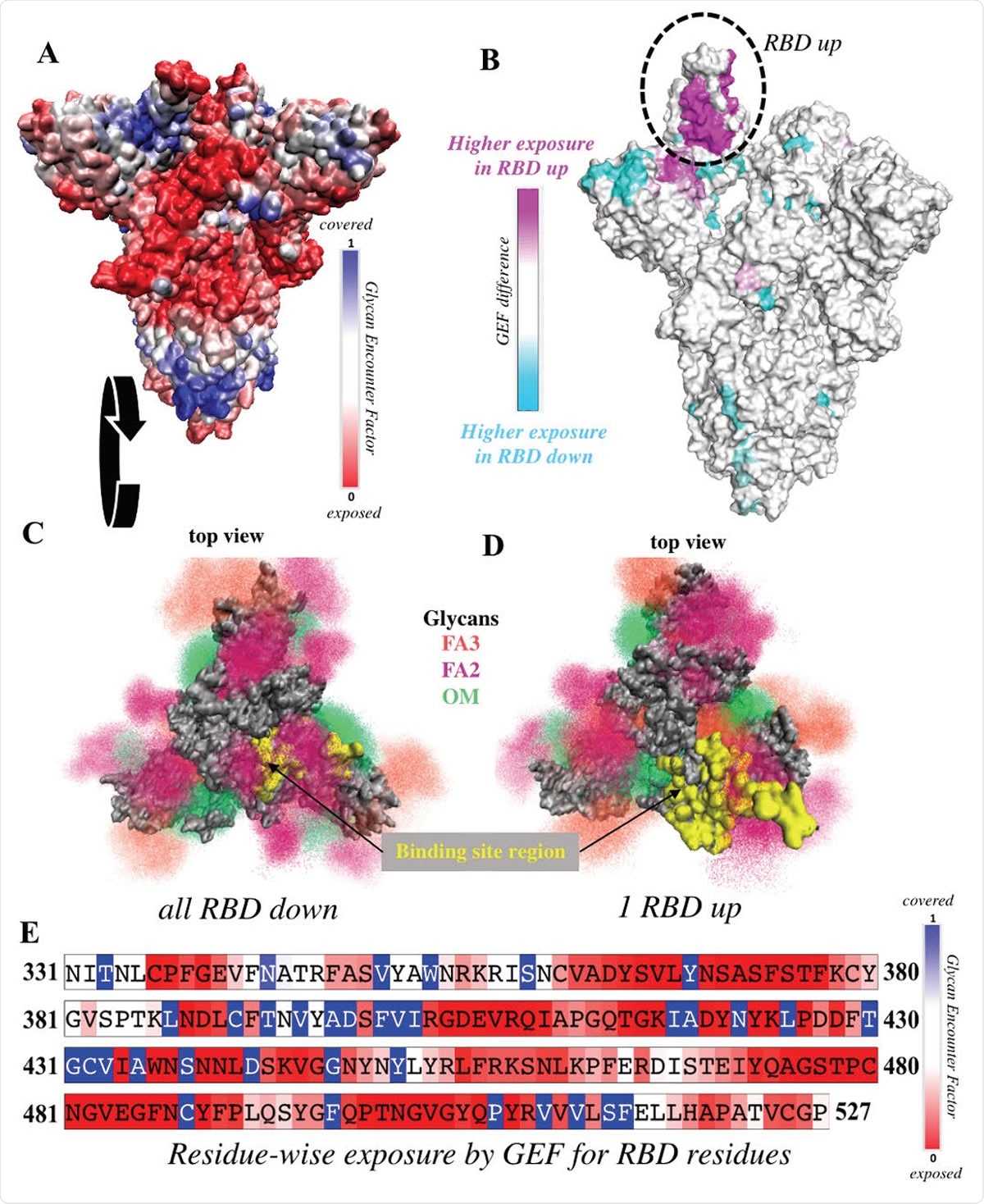 RBD is significantly more exposed in the one-up conformation. (A) Surface representation of the all-down Spike complex. Colors ranging between red, white and blue represent values for the glycan encounter factor (GEF). GEF describes relative exposure and coverage of protein surfaces. (B) Surface representation of the one-up Spike. Colors ranging between cyan, white, and magenta indicate GEF differences between the closed and open structures. The RBD in the up orientation is indicated by the dotted circle, where the originally buried (magenta) region around 458-478 is now exposed. (C-D) Top view of the Spike protein apex in (C) all-down and (D) one-up conformations. Protein surface is shown in grey. Glycan ensembles covering the protein surface are represented by point densities. Fucosylated 2 and 3 antennae complex (FA2 and FA3) glycans and oligomannose (OM) glycans are depicted in dark maroon, orange, and green. Binding site region, which includes receptor binding motif (residues 438-506) and C105 antibody binding residues (i.e. 403, 405, 406, 408, 409, 415-417, 420, 421, 449, 453, 455-460, 473-477, 486, 487, 489, 493-496, 498, 500-505), is colored yellow. These binding site residues are significantly more exposed in the one-up conformation, compared to the all-down case. (E) Residue-wise GEF of the RBD domain. Buried residues are colored blue. Exposure increases as the color changes toward white and red. RBD is significantly more exposed in the one-up conformation. (A) Surface representation of the all-down Spike complex. Colors ranging between red, white and blue represent values for the glycan encounter factor (GEF). GEF describes relative exposure and coverage of protein surfaces. (B) Surface representation of the one-up Spike. Colors ranging between cyan, white, and magenta indicate GEF differences between the closed and open structures. The RBD in the up orientation is indicated by the dotted circle, where the originally buried (magenta) region around 458-478 is now exposed. (C-D) Top view of the Spike protein apex in (C) all-down and (D) one-up conformations. Protein surface is shown in grey. Glycan ensembles covering the protein surface are represented by point densities. Fucosylated 2 and 3 antennae complex (FA2 and FA3) glycans and oligomannose (OM) glycans are depicted in dark maroon, orange, and green. Binding site region, which includes receptor binding motif (residues 438-506) and C105 antibody binding residues (i.e. 403, 405, 406, 408, 409, 415-417, 420, 421, 449, 453, 455-460, 473-477, 486, 487, 489, 493-496, 498, 500-505), is colored yellow. These binding site residues are significantly more exposed in the one-up conformation, compared to the all-down case. (E) Residue-wise GEF of the RBD domain. Buried residues are colored blue. Exposure increases as the color changes toward white and red.Change towards a higher one-up state population"In summary, our findings suggest that the overall protein exposure remains globally similar between D- and G-forms, but predicts a dramatic increase in the one-up state with the G-form," emphasize study authors in their bioRxiv paper.This means that both ACE2 binding and RBD-targeting antibody binding are expected to increase in the one-up state; hence, a change towards a higher one-up state population probably represents a dominant effect of the D614G substitution. Accordingly, such form is also predicted to be much more sensitive to neutralization due to enhanced exposure of the RBD, which is a primary target region for neutralizing antibodies. In any case, the structural data and mechanistic studies presented here, the enhanced neutralizing antibody sensitivity, as well as the experimentally determined increase in infectivity make a rather consistent story with possible therapeutic implications. *Important NoticebioRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information. |
Michael Novakhov - SharedNewsLinks℠ | InBrief |
_____________________________________________________
News Review from Michael Novakhov
_________________________________________________________________________Blogs
______________________________________________________
Saved Stories
______________________________________________________
News Review from Michael Novakhov: Blogs | Shared Stories | Michael Novakhov - SharedNewsLinks℠ |Saved Stories | Tweets |
Tweets
Comments
Post a Comment